The Annual Inspection
The campus Medical Waste Inspection by CDPH was on Wednesday, May 22, 2024. If you'd like to review the full report, please contact the biosafety officer (Bishop@ucsb.edu).
Campus was cited for 2 violations, neither of which require follow up:
1) red bags in a red bag: "The Department observed a supply of unused clean biohazard bags stored inside a biohazard bag. Immediately discontinue the use of a red biohazard bag for the purpose of storing supplies/materials. A red biohazard bag shall be used for disposal of biohazardous waste only. All items placed within a red biohazard bag are considered medical waste and must be disposed of as such [HSC § 118275(a)(2)]. In addition, all items placed into a red biohazard bag may only be removed from such bag when treatment of the waste has occurred, to eliminate a safety hazard, or by the enforcement officer in performance of an investigation pursuant to HSC § 117820 [HSC § 118280(d)]. NOTE: THE VIOLATION WAS CORRECTED AT THE TIME OF INSPECTION."
and
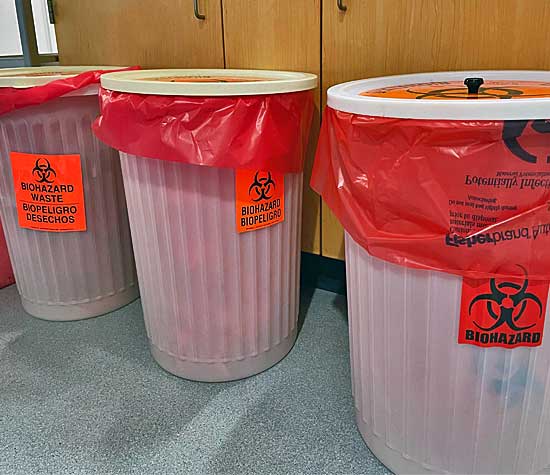
2) a solid waste container used as a table: "The Department observed items on top of biohazardous waste container restricting access to the opening of the container. Immediately discontinue placing supplies on or around the biohazardous waste container as this poses a cross-contamination hazard that places facility staff at risk from potential exposure to infectious agents. A person shall not use reusable pails, drums, dumpsters, or bins used for medical waste for the containment of solid waste, or for other purposes, except after being decontaminated by the procedures specified in [HSC] § 118295 and removal of all medical waste labels [HSC § 118305]. NOTE: THE VIOLATION WAS CORRECTED AT THE TIME OF INSPECTION."
The Regulations
Medical waste is handled according to the Medical Waste Management Act of California, California Health and Safety Code Sections 117600 - 118360, revised January 2017.
UC Santa Barbara has a Medical Waste Management Plan that conforms to federal and state regulations and University policies.The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) inspects UC Santa Barbara's medical waste program each spring.
Medical waste includes waste that is biohazardous or infectious to people. Biohazardous materials include infectious agents, samples or specimens known or suspected to be infectious, and human or primate primary cells, tissues or body fluids.
Medical waste includes biohazardous, sharps, pathology, and trace chemotherapy and pharmaceutical waste that is not regulated by the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976.
Well characterized cells transduced with replication incompetent, infectious viral vectors are considered medical waste.
Such cells may be derogated as non-medical waste after two (2) passages and transfer to a new tissue culture flask.
Medical versus Non-Medical Waste Practices
| MEDICAL / BIOHAZARDOUS / INFECTIOUS WASTE | NON-MEDICAL, "BIOTECHNOLOGY" WASTE | |
| Bag Color |
Red
|
Clear/White
|
| Examples of Solid Waste |
Primary human blood, serum, tissues Cultures of pathogenic bacteria, e.g., Salmonella app. Replication deficient viral vectors |
Recombinant E. coli K12 used to subclone human proteins. Chicken red blood cells Well-characterized human cell lines that are negative for the most common bloodborne pathogens. Recombinant tunicates Recombinant fruit files Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae
|
| Collection Container Requirements |
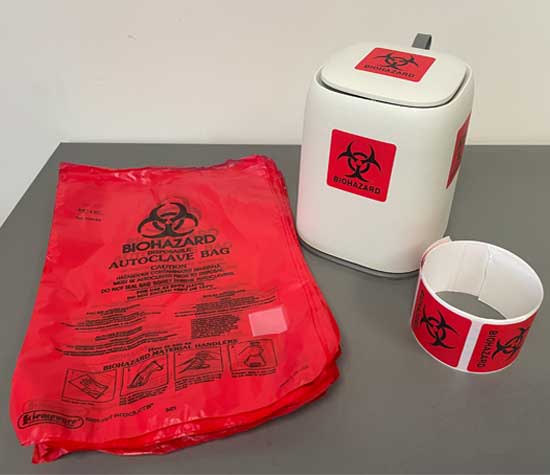
Rigid, lidded, lined with a red autoclave bag, labeled with the biohazard symbol, and surface decontaminated once a week. The color of the secondary container is not specified in the regulations. The biohazardous waste container doesn't need to be lined if not in use, however the container is still required to be lidded.
|
None |
| Bench Top Collection Container Requirements |
|
None; wire racks okay |
| Storage Container Requirements |
|
None |
| Storage Limit |
No longer than 7days at room temperature
|
None |
| Requirements for Transportation to Autoclave |
Dolly or cart, in a lidded, labeled secondary container
|
None |
| Labeling Requirements for Secondary Containers |
Biohazard label visible from all sides and on the lid
|
None |
| Treatment Specifications |
Documented run at a minimum temperature of 121℃, for at least 30 minutes in an autoclave permitted with CDPH; Alternatively, contract with a licensed medical waste hauler for treatment and disposal.
|
Best practice: 121℃ for 30 minutes. Any Autoclave |
| Signage for Solid Waste Accumulation Area |
|
None |
| Liquid Waste Treatment |
Chemically deactivated with Autoclaved without bleach
|
|
| Liquid Waste Retention Limit |
7 days at room temperature
|
None |
| Liquid Waste Disposal Procedures |
Deactivate and flush down the sink with an excess of water
|
|
| Sharps |
|
Cover and label as non-biohazardous sharps |
| Dispose of Autoclaved Solid Waste in the Lab Waste Lidded Toters |
|
 |
Waste Treatment
- Liquid medical waste may be chemically deactivated with an EPA-registered, tuberculocidal disinfectant and then discharged to the sewer system with an excess of water
- Solid medical waste is treated in an autoclave registered with CDPH at ≥ 121°C and 15 psi for at least 30 minutes or taken away for treatment by a licensed medical waste hauler. Autoclaved solid waste is disposed of in the red or brown-lidded wheeled lab waste toters.
- Biohazardous sharps are pretreated in any autoclave, picked up by the EH&S Hazardous Waste Program, and eventually sent out for incineration.
- Trace chemotherapeutics and pharmaceuticals are sent out via the EH&S Hazardous Waste Program for incineration
- Visual summary (MW pamphlet)